Home → Esophageal Manometry
Esophageal manometry is a test to measure how well the esophagus is working.
During esophageal manometry, a thin, pressure-sensitive tube is passed through your nose, down the esophagus, and into the stomach.
Before the procedure, patient is give numbing medicine inside the nose. This helps make the insertion of the tube less uncomfortable.
After the tube is in the stomach, the tube is pulled slowly back into the esophagus. At this time, the patients are asked to swallow. The pressure of the muscle contractions is measured along several sections of the tube.
While the tube is in place, other studies of the patient’s esophagus may be done. The tube is removed after the tests are completed. The test takes about 1 hour.
The patient should not have anything to eat or drink for 8 hours before the test. If the patient have the test in the morning, they are advised NOT to eat or drink after midnight.
The patients are advised to tell their health care provider about all medicines they are taking. These include vitamins, herbs, and other over-the-counter medicines and supplements.
The patient may have a gagging sensation and discomfort when the tube passes through your nose and throat. They may also feel discomfort in your nose and throat during the test.
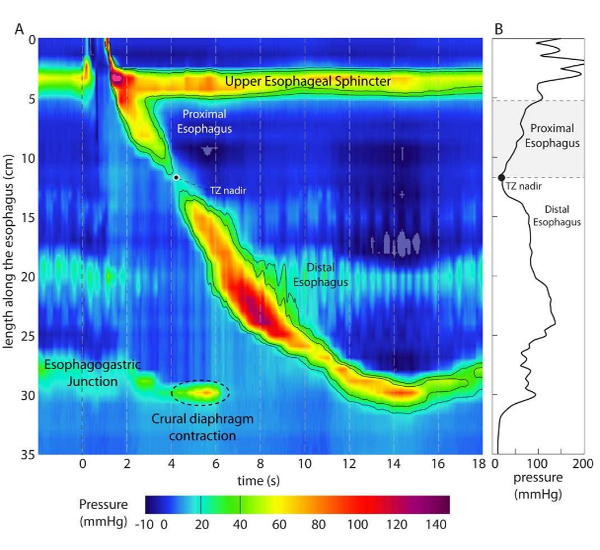
The esophagus is the tube that carries food from the mouth into the stomach. When it is swallowed, muscles in the esophagus squeeze (contract) to push food toward the stomach. Valves, or sphincters, inside the esophagus open to let food and liquid through. They then close to prevent food, fluids, and stomach acid from moving backward. The sphincter at the bottom of the esophagus is called the lower esophageal sphincter, or LES.
Esophageal manometry is done to see if the esophagus is contracting and relaxing properly. The test helps diagnose swallowing problems. During the test, the doctor can also check the LES to see if it opens and closes properly.
The test may be ordered if someone has symptoms of:
Heartburn or nausea after eating (gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD)
Problems swallowing (feeling like food is stuck behind the breast bone)
The LES pressure and muscle contractions are normal when you swallow.
Abnormal results may indicate:
A problem with the esophagus that affects its ability to move food toward the stomach (
A weak LES, which causes heartburn (GERD)
Abnormal contractions of the esophagus muscles that do not effectively move food to the stomach (
Risks of this test include:
Slight nosebleed
Sore throat
Hole, or perforation, in the esophagus (this rarely happens)