Home → Esophageal Dilation
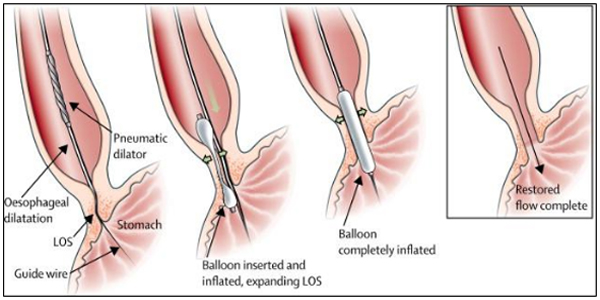
Esophageal dilation is a procedure that allows the doctor to dilate or stretch a narrowed area of esophagus (food-pipe). Doctors can use various techniques for this procedure. The doctor may perform this procedure as part of a sedated endoscopy.
The most common cause of narrowing of the esophagus or stricture, is scarring of the esophagus from reflux of stomach acid occurring in patients with heartburn. Patients with a narrowed portion of the esophagus often have trouble swallowing; food feels like it is “stuck” in the chest region, causing discomfort or pain. Less common causes of esophageal narrowing are webs or rings (which are thin layers of excess tissue), cancer of the esophagus, scarring after radiation treatment or a disorder of the way the esophagus moves.